PDF2Markdown: A big step of information processing
1. Introduction
 PDF2Markdown is an innovative conversion tool engineered to translate PDF files into the Markdown format. This tool is adept at extracting a comprehensive array of elements from PDFs, including text, images, and other content, and then meticulously converting them into a Markdown structure. The transformation to Markdown not only facilitates easier processing of the information but also enhances its organization, making it more accessible and manageable for a variety of applications.
PDF2Markdown is an innovative conversion tool engineered to translate PDF files into the Markdown format. This tool is adept at extracting a comprehensive array of elements from PDFs, including text, images, and other content, and then meticulously converting them into a Markdown structure. The transformation to Markdown not only facilitates easier processing of the information but also enhances its organization, making it more accessible and manageable for a variety of applications.
This project mainly implements the function of converting PDF to Markdown, including
- OCR: extracing text from images
- Layout Analysis: table, figure, and other layout elements
- Layout Sorting: blocks ranking
- Title Sorting: preserve hierarchy
- …
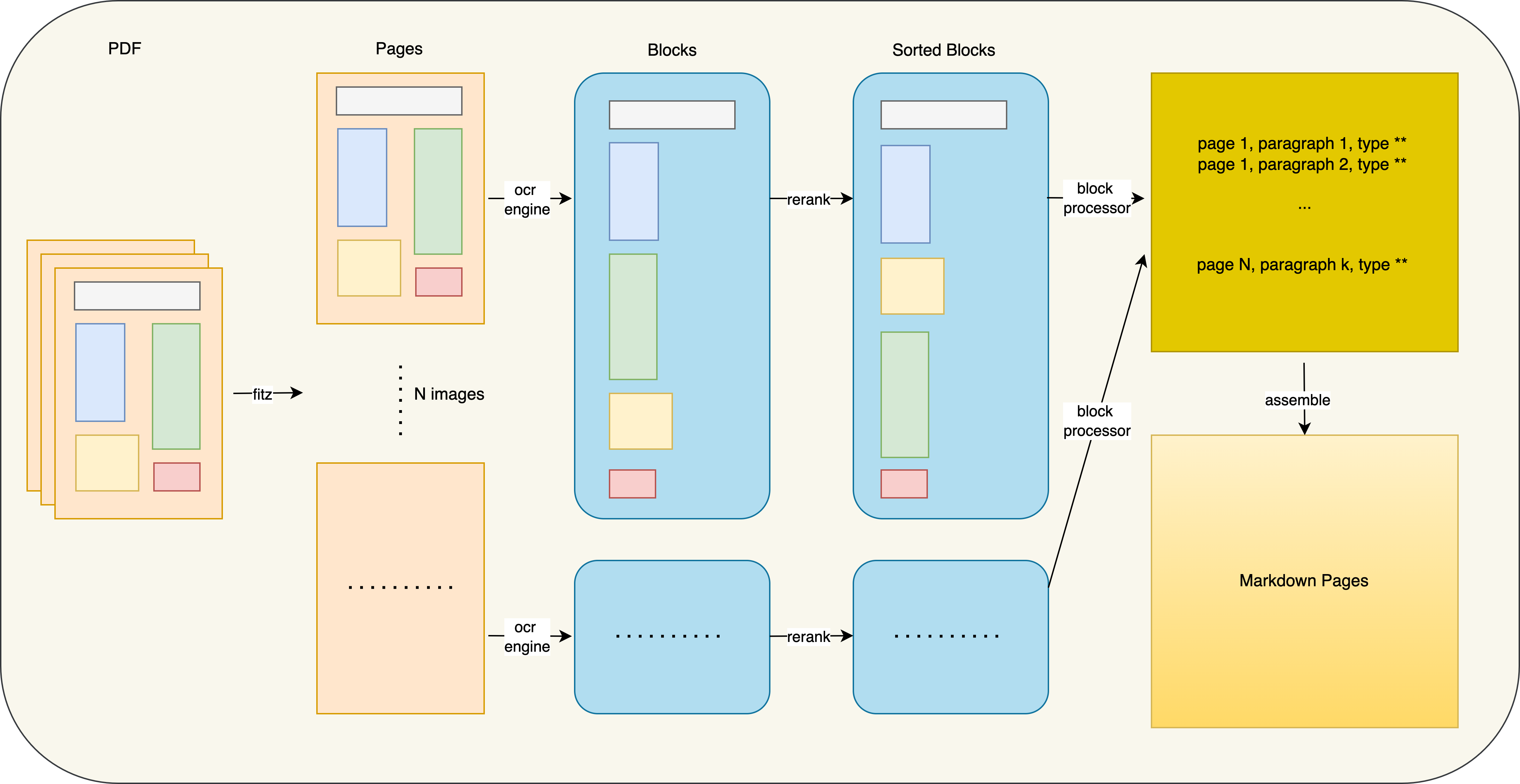
Firstly, the pdf will be converted to N images, and then perform layout analysis on each images to obtain blocks of table, title, text and etc.
Secondly, the blocks will be ranked by their position and hierarchy, and then processed by different block processors.
For each type of blocks, it’s necessary to build particular processors to extract the information from them.
After processing each blocks, the we need to combine all the information together, such that the table caption should be connected to the table, and the figure caption should be connected to the figure. Otherwise, the information that we extracted will be disordered.
Ultimately, we have successfully obtained a well-organized and finalized Markdown document.
Examples

We can see that above blocks are ranked by order of x-coordinate and y-coorinate. For each blocks, we analysis the exact types, since the defect of the model, some part may not be recognized completey.
By using our architecture and model, we have translate the pdf content to markdown file, as you can see in the below.
SGP-TOD: Building Task Bots Effortlessly via Schema-Guided LLM Prompting
Xiaoying Zhang’, Baolin Peng?*, Kun Li’, Jingyan Zhou’, Helen Meng 1The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong 2Microsoft Research, Redmond zhangxy, kunli, jyzhou, hmmeng} @ se.cuhk.edu.hk
Abstract
Building end-to-end task bots and maintaining their integration with new functionalities using minimal human efforts is a long-standing chal. lenge in dialog research. Recently large lan guage models (LLMs) have demonstrated ex- ceptional proficiency in conversational engage- ment and adherence to instructions across var- ious downstream tasks. In this work, we intro duce SGP-TOD, Schema-Guided Prompting for building Task-Oriented Dialog systems ef- fortlessly based on LLMs. Utilizing the sym- bolic knowledge - task schema, we instruct fixed LLMs to generate appropriate responses on novel tasks, circumventing the need for training data. Specifically, SGP-TOD com- prises three components: a LLM for engag- ing with users, a DST Prompter to aid the LLM with dialog state tracking, which is then used to retrieve database items, and a Pol- icy Prompter to elicit proper responses ad- hering to the provided dialog policy. Exper imental results on Multiwoz, RADDLE and STAR datasets show that our training-free strategy SGP-TOD, without any task-specific data, yields state-of-the-art (SOTA) zero-shot performance, greatly surpasses the few-shot approaches. . In a domain-extension setting, SGP-TOD aptly adapts to new functionalities by merely adding supplementary schema rules We make our code and data publicly avail. able.1
1 Introduction
Building task-oriented dialog (TOD) systems has been a long-standing challenge in artificial intelli- gence. The prevailing approach for creating task bots (Hosseini-Asl et al., 2020; Peng et al., 2021a Sun et al., 2022) is to fine-tune pre-trained language models (PLMs). such as T5 (Raffel et al.. 2020) and GPT-2 (Radford et al., 2019). Despite their great success, developing and maintaining such task bots generally requires adequate annotated data and extensive fine-tuning/re-training. Recently, large Language Models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT2 and GPT-4 (OpenAI, 2023), have revolutionized natu cal language processing (NLP) applications (Wang et al., 2023; Wei et al., 2022), owing to their re markable conversational skills (Qin et al., 2023) instruction-following abilities (Ouyang et al., 2022) and zero-shot generalization capabilities (Chowd hery et al., 2022a; Hu et al., 2022). This raises a research question: can LLMs be effectively uti lized for building task bots with minimum human efforts? A contemporary study (Hudecek and Dusek 2023) explores the potential of LLMs for rapidly
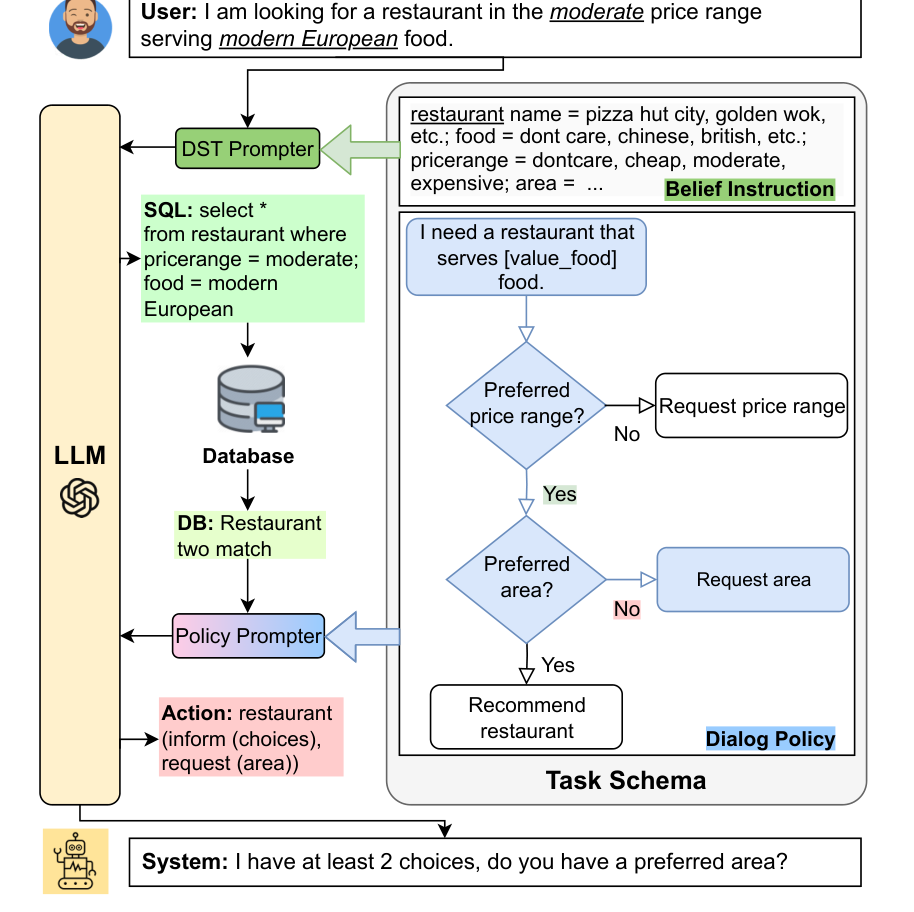 Figure 1: The proposed SGP- -TOD is depicted with dialog example, where the prompters integrate task schema (right) to assist the frozen LLM in generating an appropriate response (left).
Figure 1: The proposed SGP- -TOD is depicted with dialog example, where the prompters integrate task schema (right) to assist the frozen LLM in generating an appropriate response (left).
Conclusion
We are currently leveraging PaddleOCR along with our proprietary framework to facilitate the conversion of PDF documents into Markdown format. However, we acknowledge that there is significant potential for refinement within our process, particularly in the realms of layout analysis and the distinct processing of content blocks.